Product Description
Machining Capability
Our Gear, Pinion Shaft, Ring Gear Capabilities:
| Capabilities of Gears/ Splines | ||||||
| Item | Internal Gears and Internal Splines | External Gears and External Splines | ||||
| Milled | Shaped | Ground | Hobbed | Milled | Ground | |
| Max O.D. | 2500 mm | |||||
| Min I.D.(mm) | 30 | 320 | 20 | |||
| Max Face Width(mm) | 500 | 1480 | ||||
| Max DP | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| Max Module(mm) | 26 | 45 | 26 | 45 | ||
| DIN Class Level | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | ||
| Tooth Finish | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | ||
| Max Helix Angle | ±22.5° | ±45° | ||||
Our Main Product Range
1. Spur Gear
2. Planetary Gear
3. Metal Gears
4. CHINAMFG
5. Ring Gear
6. Gear Shaft
7. Helical Gear
8. Pinion Shaft
9. Spline Shaft
Company Profile
1. 21 years experience in high quality gear, gear shaft’s production, sales and R&D.
2. Our Gear, Gear Shaft are certificated by ISO9001: 2008 and ISO14001: 2004.
3. CHINAMFG has more than 50 patents in high quality Gear, Gear Shaft manufacturing.
4. CHINAMFG products are exported to America, Europe.
5. Experience in cooperate with many Fortune 500 Companies
Our Advantages
1) In-house capability: OEM service as per customers’ requests, with in-house tooling design & fabricating
2) Professional engineering capability: On product design, optimization and performance analysis
3) Manufacturing capability range: DIN 3960 class 8 to 4, ISO 1328 class 8 to 4, AGMA 2000 class 10-15, JIS 1702-1703 class 0 to 2, etc.
4) Packing: Tailor-made packaging method according to customer’s requirement
5) Just-in-time delivery capability
FAQ
1. Q: Can you make as per custom drawing?
A: Yes, we can do that.
2. Q: If I don’t have drawing, what can you do for me?
A: If you don’t have drawing, but have the sample part, you may send us. We will check if we can make it or not.
3. Q: How do you make sure the quality of your products?
A: We will do a series of inspections, such as:
A. Raw material inspection (includes chemical and physical mechanical characters inspection),
B. Machining process dimensional inspection (includes: 1st pc inspection, self inspection, final inspection),
C. Heat treatment result inspection,
D. Gear tooth inspection (to know the achieved gear quality level),
E. Magnetic particle inspection (to know if there’s any cracks in the gear).
We will provide you the reports 1 set for each batch/ shipment.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
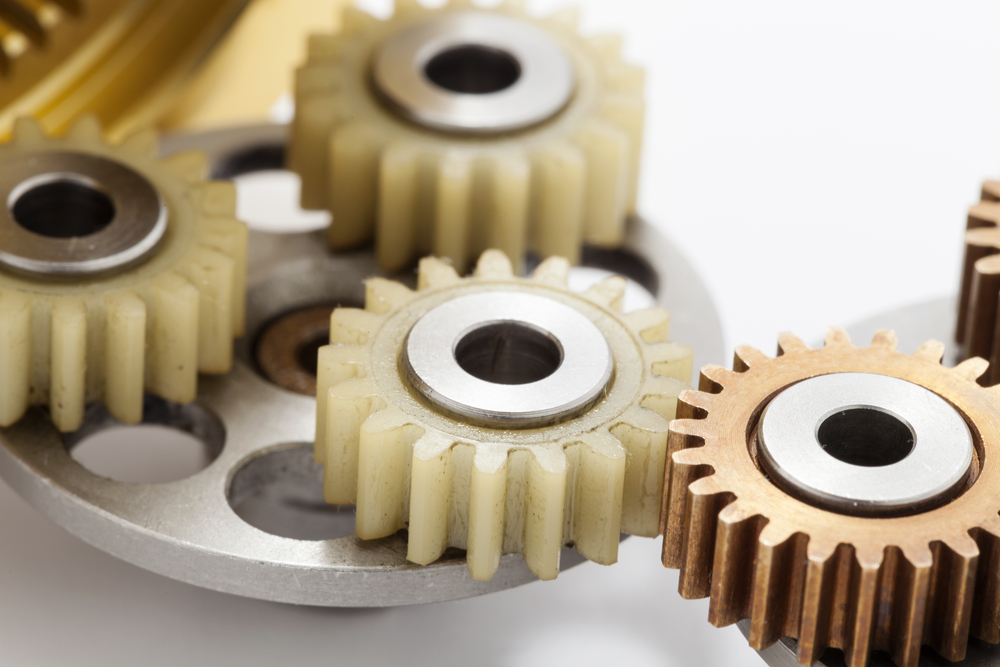
How do you choose the right type of plastic material for specific applications?
Choosing the right type of plastic material for specific applications requires careful consideration of various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process:
1. Identify Application Requirements: Begin by understanding the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, mechanical stress, electrical properties, dimensional stability, and regulatory compliance. This initial assessment will help narrow down the suitable plastic material options.
2. Research Plastic Material Properties: Conduct thorough research on different types of plastic materials and their properties. Consider factors such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, chemical resistance, electrical conductivity, impact resistance, UV stability, and food safety approvals. Plastic material datasheets and technical resources from manufacturers can provide valuable information.
3. Evaluate Material Compatibility: Assess the compatibility of the plastic material with the surrounding environment and other components in the system. Consider the potential for chemical reactions, galvanic corrosion, thermal expansion, and any specific requirements for mating surfaces or interfaces. Ensure the selected material is compatible with the intended operating conditions.
4. Consider Manufacturing Process: Evaluate the manufacturing process involved in producing the desired component or product. Different plastic materials may have specific requirements or limitations for processes such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or machining. Ensure the chosen material is compatible with the selected manufacturing method and can meet the desired quality and production efficiency.
5. Assess Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the plastic material. Some specialty or high-performance plastics may be more expensive or have limited availability compared to more common materials. Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and feasibility of using the selected material within the project’s budget and timeline.
6. Consult with Material Experts: If necessary, consult with material experts, engineers, or suppliers who have expertise in plastic materials. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their experience and knowledge of specific applications. Their input can help ensure the optimal material selection for the intended use.
7. Perform Prototype and Testing: Before finalizing the material selection, it’s advisable to produce prototypes or conduct testing using the chosen plastic material. This allows for verification of the material’s performance, dimensional accuracy, strength, durability, and other critical factors. Iterative testing and evaluation can help refine the material selection process if needed.
By following these steps and considering the application requirements, material properties, compatibility, manufacturing process, cost, and expert advice, it’s possible to choose the most appropriate plastic material for specific applications. Proper material selection is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and safety in various industries and products.

How do you prevent premature wear and degradation in plastic gears?
Preventing premature wear and degradation in plastic gears requires implementing various measures and considerations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to achieve this:
1. Material Selection: Choose a plastic material with suitable properties for the specific application. Consider factors such as strength, stiffness, wear resistance, and compatibility with operating conditions. Opt for materials that have good resistance to wear, fatigue, and environmental factors to minimize premature degradation.
2. Gear Design: Pay attention to the design of the plastic gears to minimize wear and degradation. Optimize the tooth profile, gear geometry, and load distribution to reduce stress concentrations and ensure even load sharing among the teeth. Incorporate features such as fillets, reinforcements, and optimized tooth profiles to enhance the gear’s durability.
3. Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction, minimize wear, and prevent premature degradation. Choose lubricants that are compatible with the plastic material and the operating conditions. Ensure adequate lubrication by following manufacturer recommendations and implementing proper lubrication techniques such as oil bath, grease, or dry lubrication.
4. Operating Conditions: Consider the operating conditions and make adjustments to prevent premature wear and degradation. Control operating temperatures within the recommended range for the plastic material to avoid thermal degradation. Avoid excessive speeds or loads that can lead to increased friction and wear. Minimize exposure to harsh chemicals, UV radiation, or abrasive particles that can degrade the plastic material.
5. Maintenance: Implement regular maintenance practices to prevent premature wear and degradation. Conduct periodic inspections to identify signs of wear or damage. Replace worn or damaged gears promptly to prevent further degradation. Follow recommended maintenance schedules for lubrication, cleaning, and any other specific requirements for the plastic gears.
6. Proper Installation: Ensure that plastic gears are installed correctly to minimize wear and degradation. Follow manufacturer guidelines and recommendations for installation procedures, such as proper alignment, torque values, and fastening techniques. Improper installation can lead to misalignment, increased stress concentrations, and accelerated wear.
7. Optimized Load Distribution: Design the gear system to ensure even load distribution across the gear teeth. Consider factors such as tooth profile, tooth width, and the number of teeth to optimize load sharing. Uneven load distribution can lead to localized wear and premature degradation of specific gear teeth.
8. Environmental Protection: Protect plastic gears from harsh environmental conditions that can accelerate wear and degradation. Implement measures such as sealing mechanisms, coatings, or encapsulation to shield the gears from exposure to chemicals, moisture, UV radiation, or abrasive particles.
9. Quality Manufacturing: Ensure high-quality manufacturing processes to minimize defects and inconsistencies that can compromise the durability of plastic gears. Use reputable suppliers and manufacturers that adhere to strict quality control measures. Conduct thorough inspections and testing to verify the quality of the gears before installation.
By considering these preventive measures, such as material selection, gear design, lubrication, operating conditions, maintenance, proper installation, load distribution optimization, environmental protection, and quality manufacturing, it’s possible to minimize premature wear and degradation in plastic gears, ensuring their longevity and performance.

What are plastic gears and how are they used?
Plastic gears are gear components made from various types of polymers or plastic materials. They offer unique properties and advantages compared to traditional metal gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of plastic gears and their applications:
- Types of Plastic Materials: Plastic gears can be manufactured from different types of polymers, including thermoplastics such as acetal (polyoxymethylene – POM), nylon (polyamide – PA), polycarbonate (PC), and polyethylene (PE), as well as thermosetting plastics like phenolic resins. Each material has its own specific characteristics, such as strength, wear resistance, and temperature resistance, which make them suitable for different applications.
- Advantages of Plastic Gears: Plastic gears offer several advantages over metal gears, including:
- Lightweight: Plastic gears are lighter in weight compared to metal gears, which can be beneficial in applications where weight reduction is important.
- Low Noise and Vibration: Plastic gears can provide quieter operation due to their inherent damping properties that reduce noise and vibration levels.
- Corrosion Resistance: Certain plastic materials used in gear manufacturing exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for applications in corrosive environments.
- Self-Lubrication: Some plastic materials have self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for external lubrication and simplifying maintenance.
- Cost-Effective: Plastic gears can be more cost-effective compared to metal gears, especially in large-scale production, due to the lower material and manufacturing costs.
- Applications of Plastic Gears: Plastic gears find applications in various industries and systems, including:
- Automotive: Plastic gears are used in automotive systems such as windshield wipers, HVAC systems, seat adjusters, and electric power steering systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Plastic gears are commonly found in consumer electronics like printers, scanners, cameras, and home appliances.
- Medical Devices: Plastic gears are used in medical equipment and devices where weight reduction, low noise, and corrosion resistance are desired.
- Toy Manufacturing: Plastic gears are extensively used in the production of toys, including mechanical toys, hobby models, and educational kits.
- Office Equipment: Plastic gears are employed in office equipment like printers, copiers, and scanners, where quiet operation and cost-effectiveness are important.
- Industrial Machinery: Plastic gears can be utilized in various industrial machinery applications, such as conveyor systems, packaging equipment, and textile machinery.
It’s important to note that while plastic gears offer unique advantages, they also have limitations. They may not be suitable for applications requiring extremely high torque, high temperatures, or where precise positioning is critical. The selection of plastic gears should consider the specific requirements of the application and the mechanical properties of the chosen plastic material.


editor by CX 2024-04-10